When a person drinks alcohol excessively, they may not realized their increased risk of developing a substance use disorder. Many factors contribute to the risk factors of developing and (alcohol use disorder), from family history to environmental influences, research shows developing an alcohol problem is linked to genetic predisposition.
Understanding the interplay of genetic risk, environmental impacts, and individual behaviors is essential in addressing the complexities of alcoholism and providing effective treatment options. If you suspect that your or your family member may be struggling with alcohol use disorder, Malibu Detox and Residental Treatment Center is here to help.
What Is an Alcohol Use Disorder?

Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), often referred to as alcoholism, is a serious medical condition characterized by the compulsive consumption of alcohol despite its negative consequences. It falls under the broader category of substance use disorders, which encompass various forms of substance abuse.
AUD can have both genetic and environmental factors at play in its development. Research from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) indicates that about 50% of a person’s risk for developing AUD is linked to genetic predisposition, while the other portion is influenced by social and environmental impacts.
What Developing Alcoholism Can Look Like

When you develop an addiction, it is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Recognizing the warning signs is essential to provide help to those in need.
One of the key indicators of developing alcoholism is problematic drinking behavior. This can manifest as an increasing tolerance to alcohol, where an individual needs more to achieve the desired effect.
Alongside this, there may be a loss of control over alcohol consumption, leading to frequent episodes of binge drinking. As alcohol tolerance progresses, individuals may prioritize drinking over other aspects of life, such as work, relationships, or personal responsibilities.
When individuals abuse alcohol, they may notice aggressive behavior or a worsening of existing mental disorders. For example, alcohol abuse can worsen bipolar disorder by intensifying mood swings, interfering with medication effectiveness, promoting impulsive behaviors, increasing the risk of suicide, and complicating treatment efforts.
Genetics of Alcohol Use Disorder
Individuals with a family history of alcohol use disorders are at an increased genetic risk for developing AUD. Specific genes, including those involved in alcohol metabolism and the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) pathway, have been implicated in this process.
Twin studies, particularly those involving identical twins, have highlighted the genetic component of AUD, showing a higher concordance rate among genetically identical individuals.
Is There an Alcohol Addiction Gene?

The question of whether there is a single “alcoholic gene” is a topic that has intrigued researchers for years. However, the answer is not as straightforward as a simple yes or no. Instead, the genetics of alcohol use disorder are intricate, involving multiple genes and complex interactions with environmental factors.
Research, including studies from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA), has shown that genetic factors indeed play a significant role in an individual’s susceptibility to abusing alcohol. However, there isn’t a single specific gene responsible for alcoholism.
Instead, it’s a polygenic trait, meaning it involves multiple genes, each with a small effect. These genes are associated with various aspects of alcohol metabolism, the reward system in the brain, and other factors that influence drinking behaviors.
This understanding underscores the importance of a holistic approach to addressing alcohol addiction, considering both genetic predisposition and environmental factors when providing treatment and support to individuals seeking help for their alcohol use disorders.
Organizations like American Addiction Centers specialize in offering comprehensive treatment guides and other resources that take into account these multifaceted aspects of alcohol addiction.
However, it’s important to note that genetics alone do not determine a person’s destiny regarding AUD. Gene and environment interactions play a crucial role, emphasizing the need for a holistic approach to understanding and addressing this complex disorder.
Environmental Factors for Alcohol or Substance Abuse
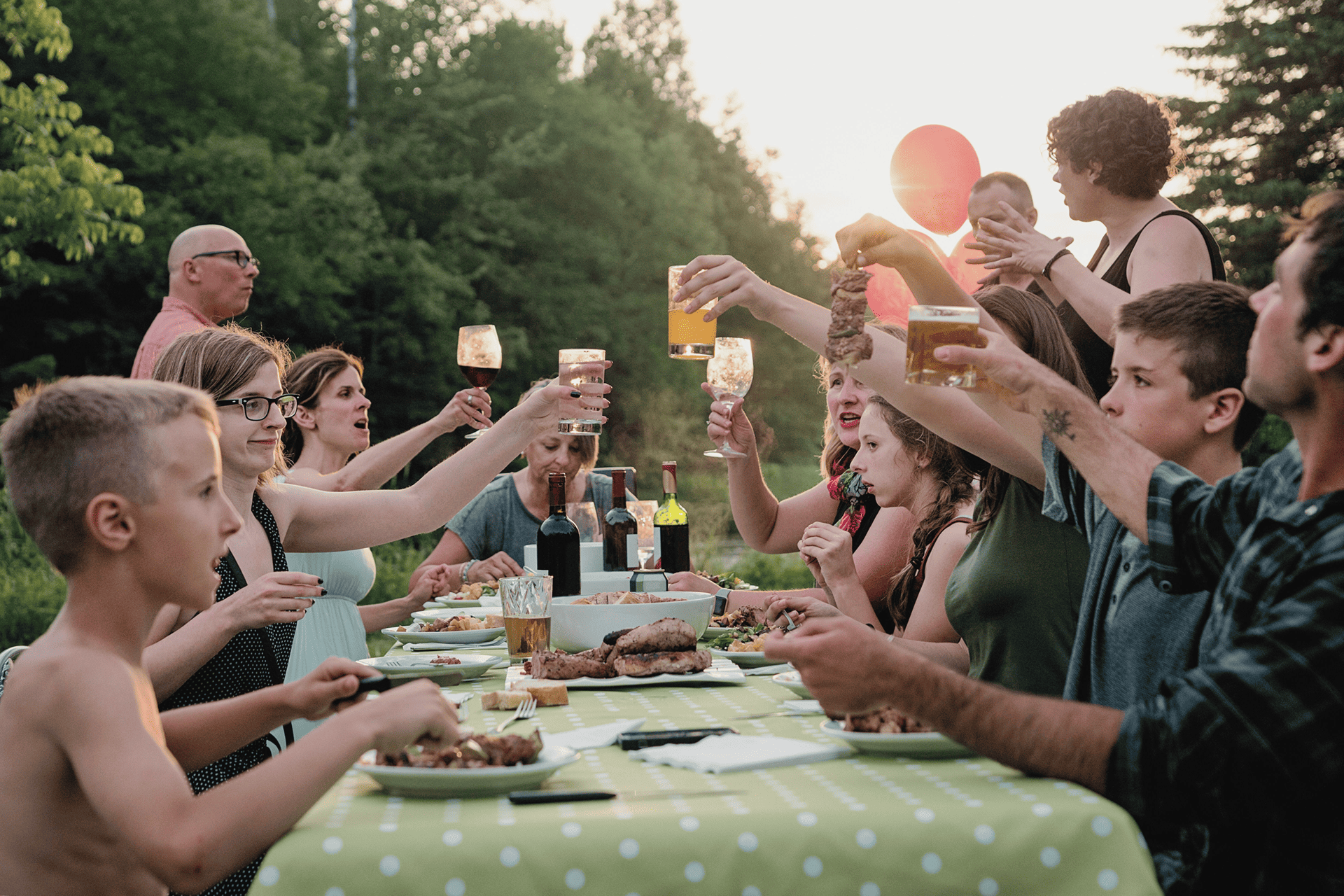
While genetics contribute to about half of the risk, the other half is influenced by social and environmental factors, such as upbringing, peer influences, and exposure to traumatic experiences.
The children of parents who struggle with substance abuse can have an increased risk of drinking alcohol to excess, as well as a risk of drug abuse. Families that are disrupted or have consistent displays of substance abuse can play a large role in increasing the risk of developing alcohol use disorder in their children.
Aside from the risk that “addiction genes” impose on a person, growing up in a situation in which a family member regularly abuses drugs or alcohol can normalize this behavior and make it more difficult for individuals to identify if and when they are at risk of addiction.
Mitigating Risks of Alcohol Abuse Despite Genetics
Moderation is Key: Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels, adhering to recommended guidelines for safe drinking. This reduces the risk of developing problematic drinking behaviors.
Awareness of Family History: Understand your family’s history of alcoholism, as genetics can play a role. Being aware of your genetic predisposition can help you make informed choices about alcohol consumption and seek support when needed.
Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Develop alternative coping strategies for stress, anxiety, and emotional challenges. Explore healthier outlets like exercise, meditation, or talking to a therapist to manage emotions without turning to drinking.
Social Support: Maintain a strong support system of friends and family who are aware of your goals to avoid alcoholism. They can provide encouragement and help you stay accountable.
Seek Professional Help: If you suspect you may have a greater risk of alcoholism or are struggling with alcohol abuse, don’t hesitate to reach out to our treatment center for professional help. Studies and guides from American Addiction Centers can provide tailored advice to address both genetic and environmental factors in your journey to recovery.
Find Help for Alcohol Use Disorder Today

At Malibu Detox and Residental Treatment Center, we offer a wide range of options that are tailored to best assist you or your loved one through the recovery journey.
We provide evidence-based treatment methods along with dual-diagnosis treatment and aftercare to ensure you are supported throughout recovery. Take the first step toward recovery and contact us today. Call (424) 234 2027.





